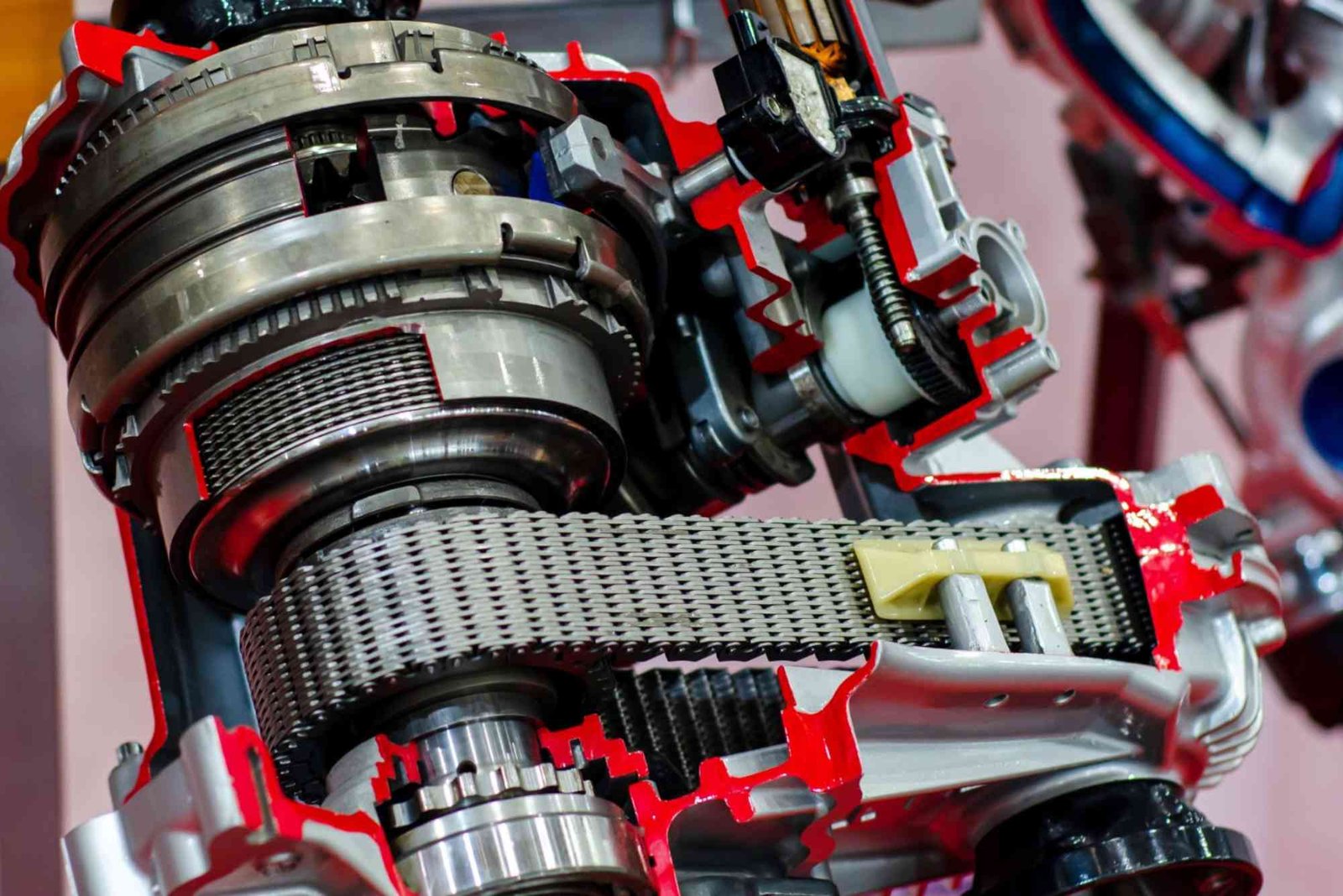
If you’ve ever wondered what makes a four-wheel-drive vehicle so capable on rough terrain, the answer often lies in the transfer case. Understanding what a transfer case does and how it functions is essential for anyone interested in automotive systems. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll break down what is transfer case in automobiles, how it works, and why it’s such an integral part of vehicles equipped with 4WD and AWD systems.
Understanding the Transfer Case
A transfer case is a critical component found in four-wheel-drive (4WD) and all-wheel-drive (AWD) vehicles. It is responsible for transferring power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles, ensuring that all wheels receive torque when needed. This mechanism improves traction and stability, especially in off-road conditions or slippery surfaces like snow, mud, and sand.
In simple terms, when you engage your vehicle’s 4WD mode, the transfer case distributes power evenly between the front and rear wheels. This function allows your vehicle to maintain grip and control, which is especially important for off-road adventures or challenging driving conditions.
How Does a Transfer Case Work?
The transfer case connects directly to the vehicle’s transmission and uses a set of gears, chains, or sometimes both, to distribute torque. It operates through a driveshaft that delivers power to the front and rear differentials. Depending on the type of transfer case, power distribution can be either full-time or part-time.
In full-time 4WD systems, the transfer case continuously sends power to all four wheels, providing constant traction. In contrast, part-time 4WD systems allow drivers to switch between two-wheel drive (2WD) and 4WD modes. This manual control can enhance fuel efficiency when 4WD isn’t necessary, such as during highway driving.
Modern transfer cases often use electronic controls, allowing drivers to switch modes at the push of a button rather than relying on mechanical levers. This innovation not only improves convenience but also ensures smooth transitions between different drive modes.
Types of Transfer Cases
While there are several designs, transfer cases generally fall into two main categories: chain-driven and gear-driven.
Chain-driven transfer cases are lightweight, quieter, and commonly found in everyday SUVs and crossover vehicles. They provide reliable performance for daily driving and light off-roading.
Gear-driven transfer cases, on the other hand, are heavier and more robust, making them ideal for heavy-duty trucks and off-road vehicles. These systems are built to handle extreme torque loads and rugged terrains.
Some modern transfer cases also incorporate advanced features like torque vectoring, which optimizes power distribution between axles for enhanced handling and efficiency.
Functions of a Transfer Case
A transfer case serves several important roles in an automobile beyond simply distributing power. It synchronizes rotational speeds between the front and rear wheels to prevent drivetrain strain. Additionally, it offers low-range gearing, which provides extra torque at low speeds—crucial for climbing steep inclines or navigating through rough terrain.
In AWD vehicles, the transfer case also helps manage traction automatically. Sensors monitor wheel slip and adjust power distribution in real time. This ensures that your vehicle remains stable and responsive, even in unpredictable driving conditions.
Another important function is maintaining proper lubrication and cooling of the internal components. Transfer cases use special fluid that keeps gears and chains operating smoothly. Regular maintenance, such as checking and replacing this fluid, is vital for preventing wear and ensuring longevity.
Common Transfer Case Problems
Like any mechanical system, a transfer case can experience wear over time. One of the most common issues is fluid leakage, often caused by worn seals or gaskets. Without proper lubrication, the internal gears and bearings may grind, leading to costly damage.
Drivers might also notice unusual noises, such as grinding or humming sounds, especially when shifting between drive modes. This can indicate low fluid levels or internal wear. Difficulty engaging 4WD or an illuminated warning light on the dashboard can also signal transfer case issues.
Ignoring these warning signs can result in more severe drivetrain problems. Therefore, it’s essential to schedule regular inspections and fluid replacements according to your vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations.
For professional guidance, refer to trusted sources such as the NHTSA – Vehicle Maintenance, which provides official guidelines for proper vehicle upkeep.
Maintenance Tips for Your Transfer Case
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your transfer case and ensure reliable performance. Regularly check for leaks under the vehicle, especially after driving off-road. Replace the transfer case fluid at intervals specified in your owner’s manual. Clean fluid ensures that internal gears and bearings are well-lubricated and protected from wear.
Additionally, if your vehicle allows manual shifting between 2WD and 4WD, engage the system periodically. Doing so keeps the mechanical parts moving freely and prevents them from seizing due to inactivity.
During winter or off-road conditions, pay attention to how your transfer case responds. If you notice any delay or noise when switching drive modes, have it inspected immediately. Routine care can prevent major mechanical failures and maintain your vehicle’s overall safety.
Benefits of a Transfer Case
A transfer case offers multiple advantages for drivers who encounter diverse road conditions. It improves traction by delivering power to all four wheels, reducing the risk of getting stuck in mud or snow. It also enhances vehicle control on steep slopes and loose surfaces, making it invaluable for off-road enthusiasts and drivers in challenging climates.
Furthermore, by allowing the driver to switch between 2WD and 4WD modes, the transfer case optimizes fuel efficiency and drivetrain performance. Vehicles equipped with a well-maintained transfer case typically exhibit better handling, stability, and safety.
In AWD systems, the transfer case enhances everyday driving comfort by adjusting power distribution seamlessly, ensuring smooth operation regardless of the road surface.
Real-World Example of Transfer Case Use
Imagine you’re driving a pickup truck up a steep mountain trail. In standard 2WD mode, your rear tires might struggle for grip on loose gravel. However, once you engage 4WD, the transfer case splits the power between the front and rear wheels. This distribution ensures that all tires work together, helping the vehicle climb steadily without slipping.
This practical function is what makes transfer cases so valuable for outdoor adventurers and professionals who rely on their vehicles for tough terrains. Understanding this mechanism can help you appreciate the engineering behind reliable off-road performance.
Why Understanding Transfer Cases Matters
Knowing what is transfer case in automobiles helps you make better decisions when buying or maintaining a 4WD or AWD vehicle. Whether you’re an off-road enthusiast or simply want better control on slippery roads, understanding this component empowers you to keep your vehicle in optimal condition.
Learning about the transfer case also deepens your general automotive knowledge. For more detailed information, you can learn about what is transfer case in automobiles or explore additional automobile insights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the purpose of a transfer case in a car?
The transfer case distributes power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles, enabling 4WD or AWD functionality.
2. How often should transfer case fluid be changed?
Most manufacturers recommend changing the fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, depending on driving conditions and vehicle use.
3. Can a transfer case fail completely?
Yes, if neglected, internal damage or fluid loss can cause the transfer case to fail, potentially immobilizing your vehicle.
4. What are signs of a bad transfer case?
Common symptoms include grinding noises, difficulty shifting into 4WD, fluid leaks, or warning lights on the dashboard.
5. Can you drive with a bad transfer case?
Driving with a damaged transfer case can cause further drivetrain issues and is not recommended. Seek immediate repair to prevent costly damage.
A transfer case is far more than just a mechanical link—it’s the heart of your vehicle’s 4WD or AWD system. It ensures balanced power distribution, improved traction, and enhanced control across diverse terrains. By understanding what is transfer case in automobiles, you can better maintain your vehicle and ensure dependable performance wherever you drive.
If you’re passionate about vehicle care or want to expand your automotive knowledge, explore more automobile insights and keep your car in top shape for every journey ahead.